
A diagram showing the Central Nervous System (CNS) and a flowchart explaining how it sends ou
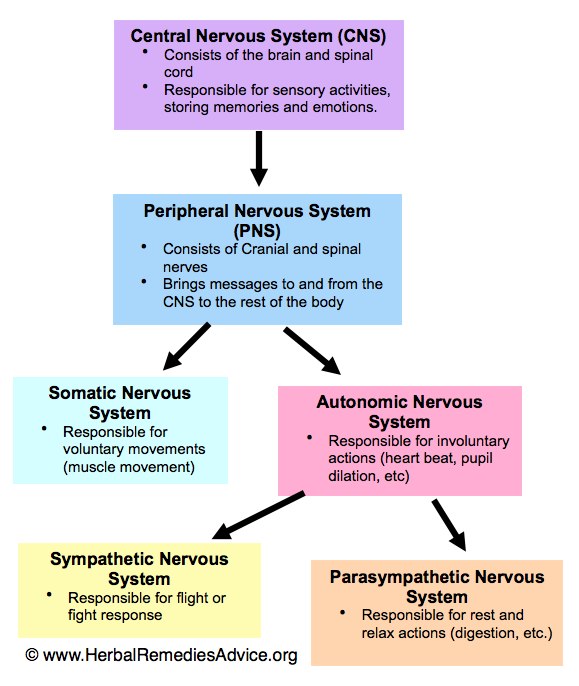
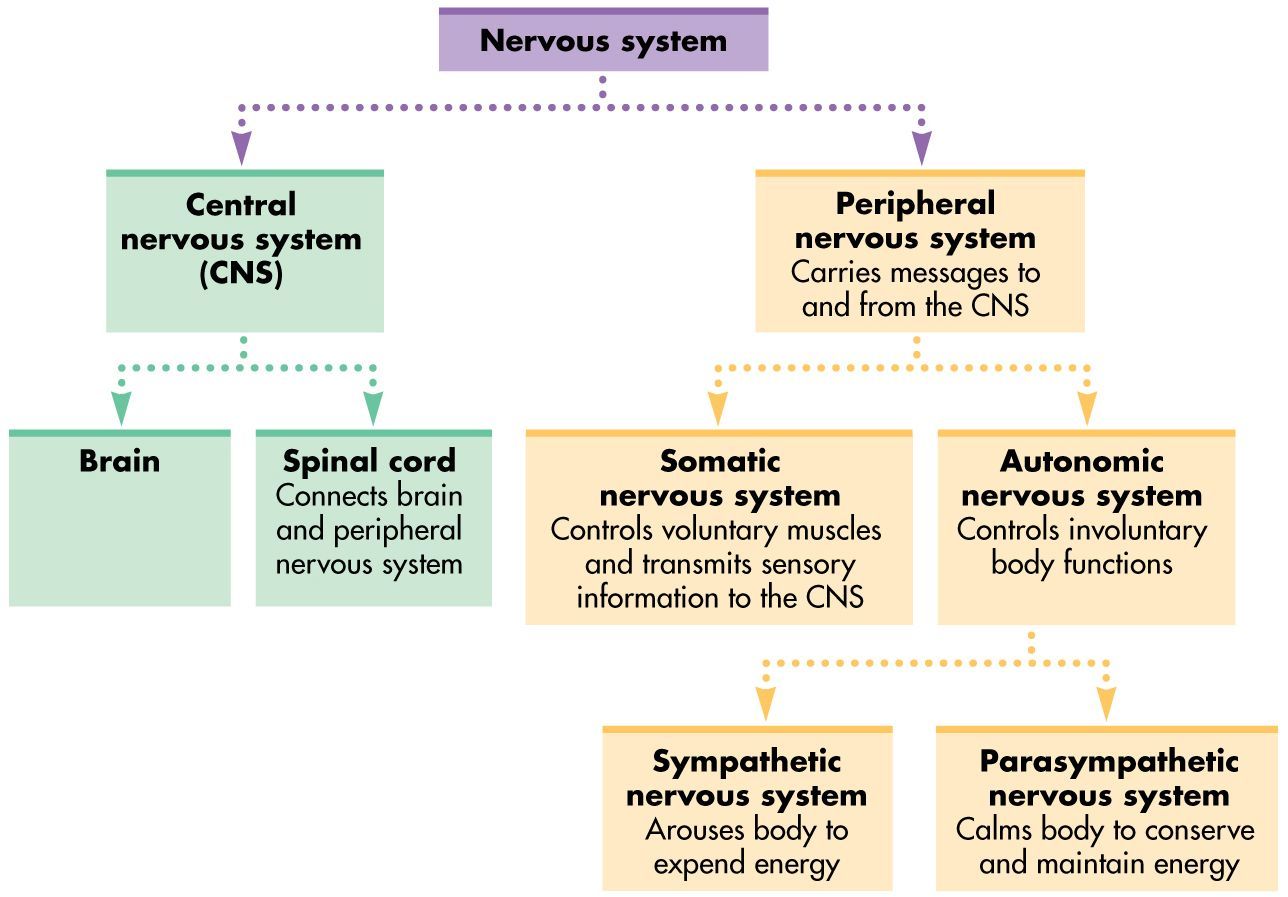
The nervous system has two major parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is.
Structure of the Nervous System
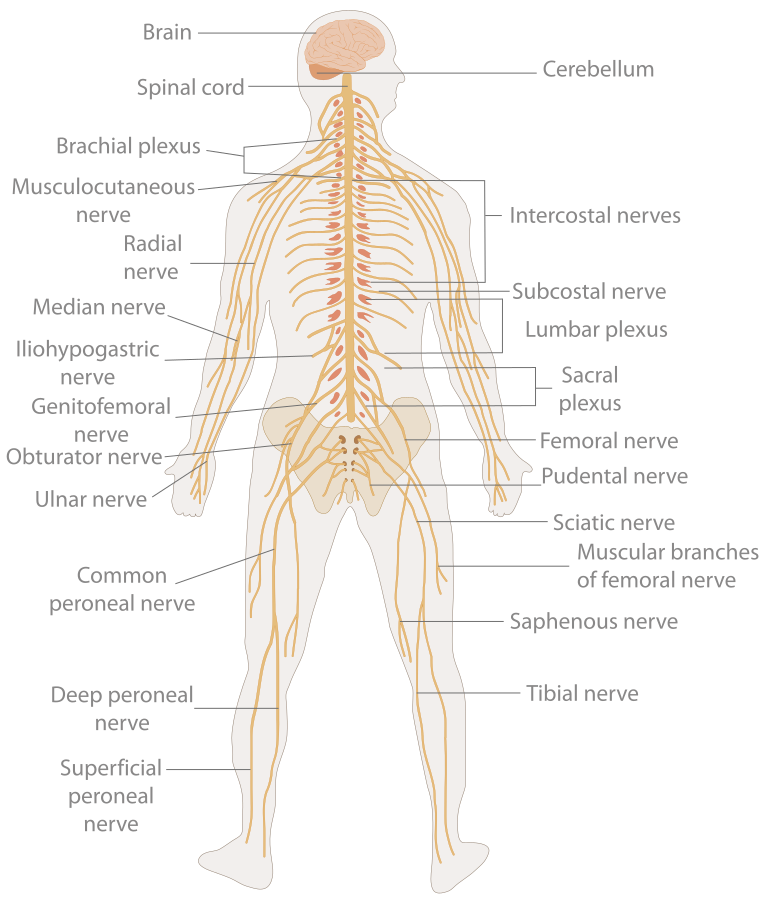
the system is the body's prime communication coordination network. It is so vast and complex that, estimate is that all the individual from one body, joined end to reach around the world two and times. The Brain and Spinal Cord are Nervous System. Nerves and Sensory Organs Make Peripheral Nervous System.
8.2 Introduction to the Nervous System Human Biology
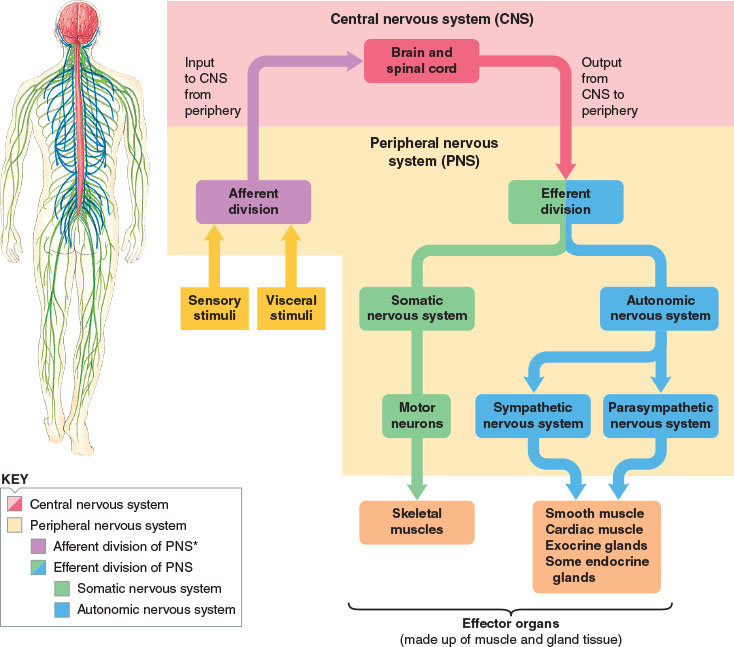
Peripheral Nervous System. The PNS is composed of neural components that extend from the aspects of the CNS. The 2 divisions of the PNS are the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the ANS ANS The ans is a component of the peripheral nervous system that uses both afferent (sensory) and efferent (effector) neurons, which control the functioning of the internal organs and involuntary processes via.

The Nervous System Serendip Studio Medical school organization, Anatomy, Human anatomy and
The nervous system, illustrated in Figure 11.2. 2, is the human organ system that coordinates all of the body's voluntary and involuntary actions by transmitting electrical signals to and from different parts of the body. Specifically, the nervous system extracts information from the internal and external environments using sensory receptors.
The Nervous System SHEN Centre for Health and Wellness
Table 11.2.1 11.2. 1: Name of structures depend on the location. A group of neuron cell bodies within the gray matter is called a nucleus in the CNS and a ganglion in the PNS. A bundle of axon within the white matter is called a tract or column in the CNS, and a nerve or nerve fiber in the PNS. CNS.

Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Parts and Function
Nervous tissue, present in both the CNS and PNS, contains two basic types of cells: neurons and glial cells. A glial cell is one of a variety of cells that provide a framework of tissue that supports the neurons and their activities.
Human Nervous System Diagram How It Works Live Science
Below the arachnoid mater is the cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF. This fluid cushions the entire central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and continually circulates around these structures to remove impurities. The pia mater is a thin membrane that hugs the surface of the brain and follows its contours. The pia mater is rich with veins and.
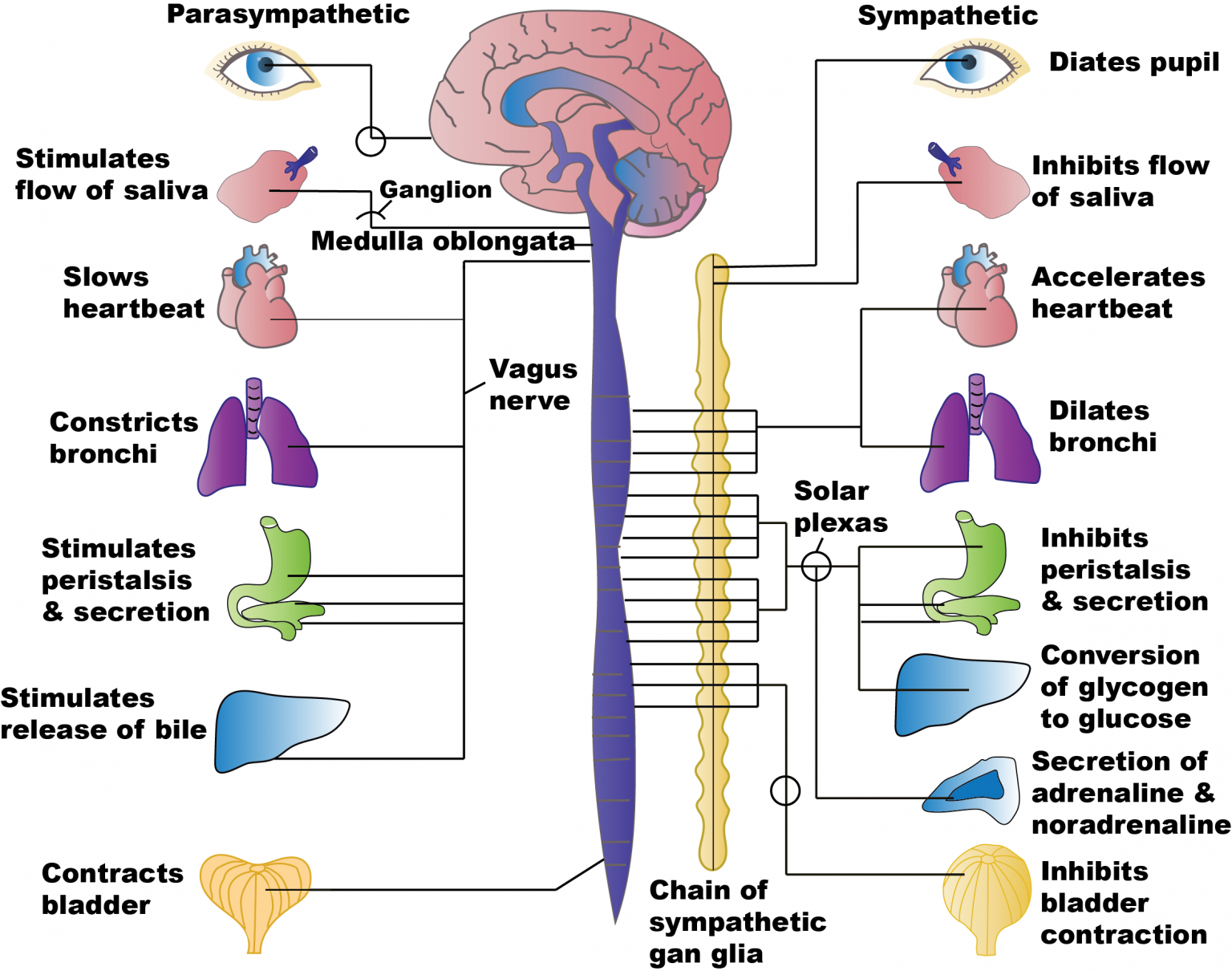
4.2 Autonomic Nervous System Basics Nursing Pharmacology
The nervous system is a network of special cells, neurons and ganglia, that work together to carry out the transmission and reception of signals between different parts of our body. The signals are transmitted in the form of electrochemical waves or chemicals.
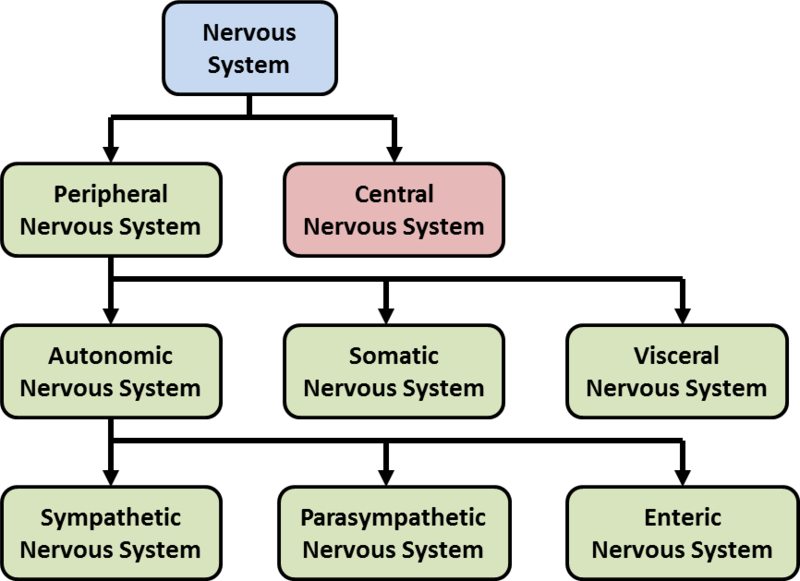
Nervous system MEpedia
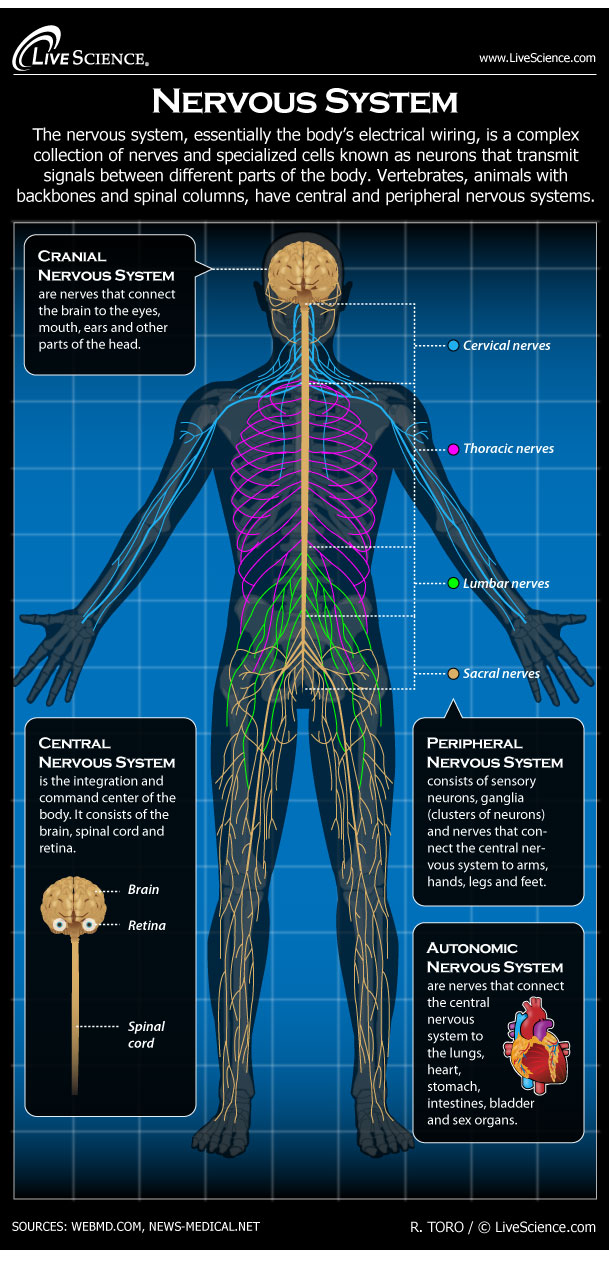
The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of the brain, spinal cord, and cerebellum. The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and neurons that communicate either between subdivisions of the PNS or connect the PNS to the CNS. The Human Nervous System: The major organs and nerves of the human nervous system.
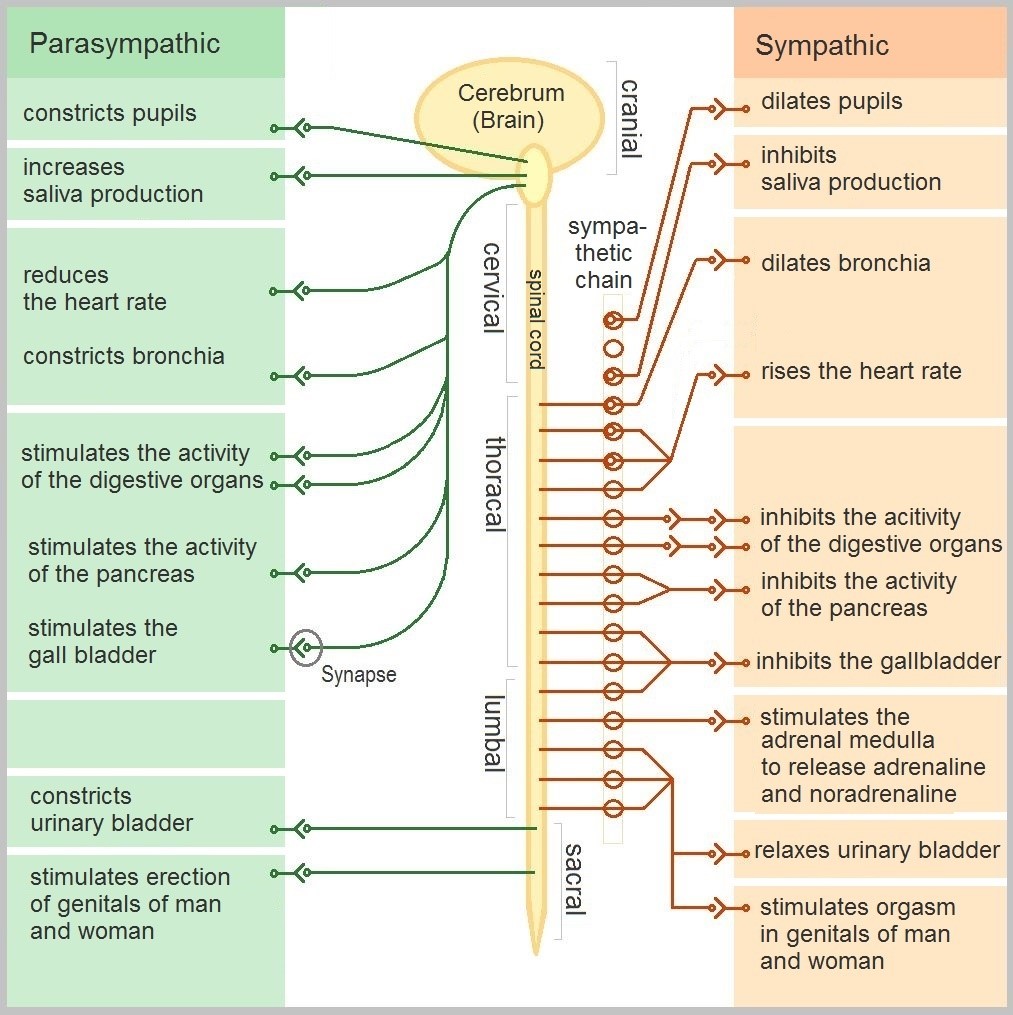
8.6 Peripheral Nervous System Human Biology
The nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body. This property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions ( heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements.

Structure of the Nervous System Psychology tutor2u
Flowchart illustrating the human nervous system. Learn how the nerves and the cells carry messages to and from the brain with this nervous system flowchart.
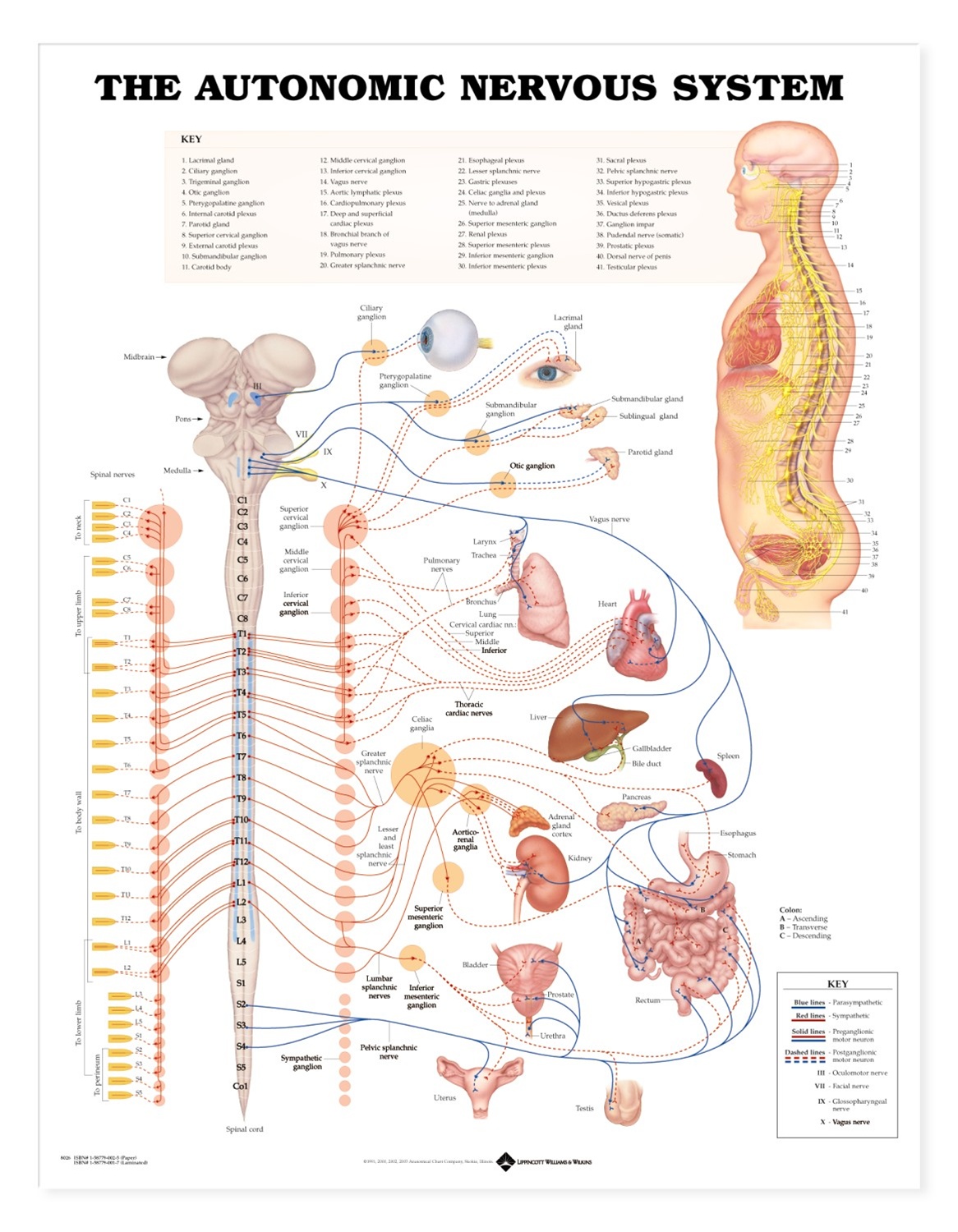
the central nervous system consists of
NOTES NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY osms.it/nervous-system-anatomy-physiology THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Network of brain, spinal cords, nerves Sensory/afferent, integrative, motor/efferent functions Sensory/afferent Receptors monitor external, internal environment Conscious stimuli (e.g. vision, hearing, touch) Unconscious stimuli (e.g. pH, blood pressure) Integrative.
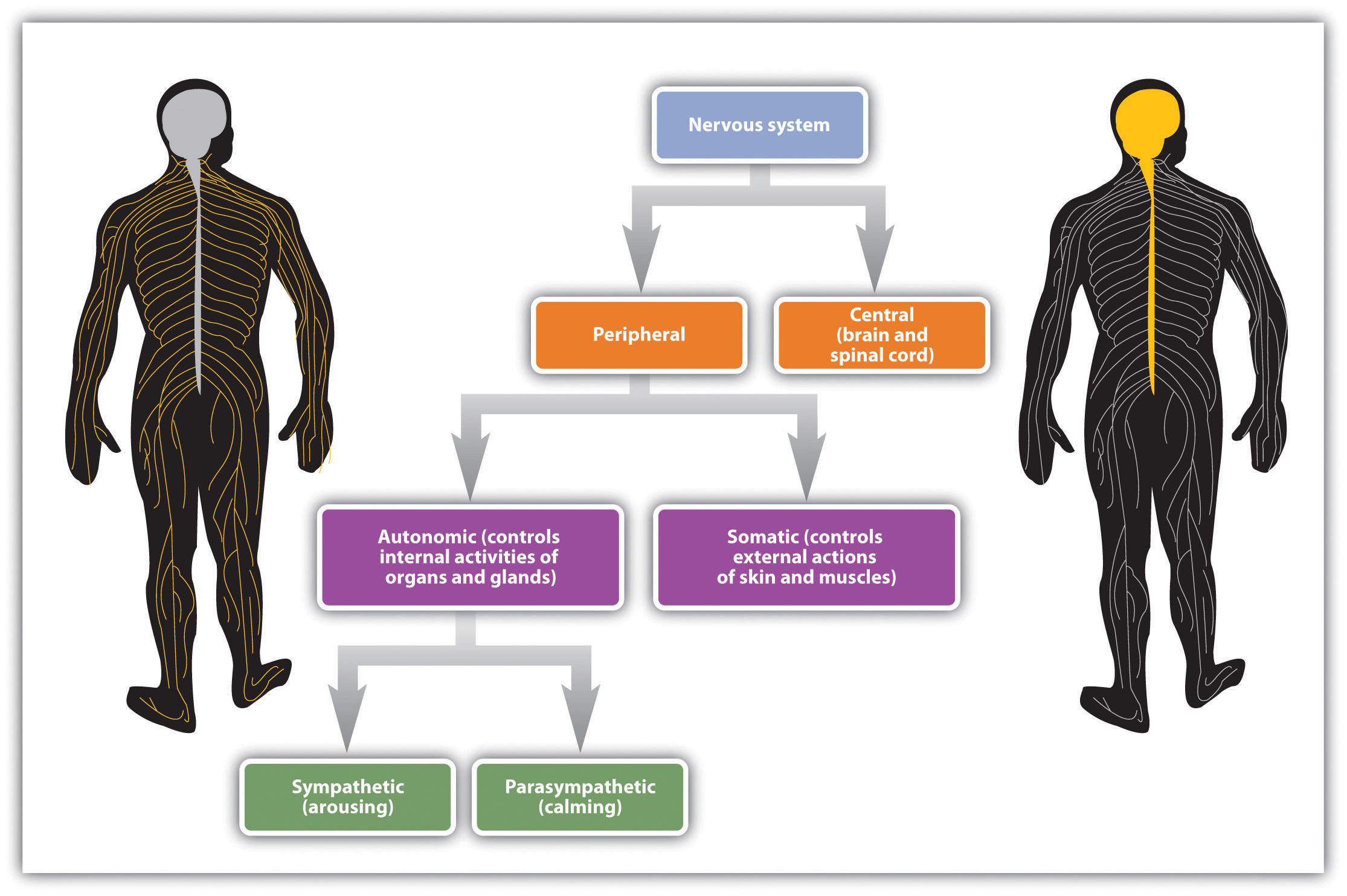
5.3 Putting It All Together The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Introduction to
The nervous system produces a response in effector organs (such as muscles or glands) due to the sensory stimuli. The motor ( efferent) branch of the PNS carries signals away from the CNS to the effector organs. When the effector organ is a skeletal muscle, the neuron carrying the information is called a somatic motor neuron; when the effector.

ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology The Nervous System and Sense Organs A Plus Topper
. The signal passes chemically across the synapse to the next neurone where the electrical impulse continues. This diagram summarises how information flows from receptors to in the nervous.
Nervous System Diagram, Function & Diseases StudiousGuy
Your nervous system's main function is to send messages from various parts of your body to your brain, and from your brain back out to your body to tell your body what to do. These messages regulate your: Thoughts, memory, learning and feelings. Movements (balance and coordination).

Unit 9 The Nervous System Douglas College Human Anatomy & Physiology I (2nd ed.)
The nervous system, essentially the body's electrical wiring, is a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body..